OpenAI has officially launched GPT-5-Codex, a specialized version of its advanced AI model, meticulously optimized for autonomous software development and coding tasks. Announced early this morning, GPT-5-Codex represents a significant leap forward in AI-assisted programming, capable of not only rapid interactive responses but also extended, independent execution of complex software engineering projects.
The training of GPT-5-Codex has been intensely focused on real-world software engineering challenges. This specialized model excels in code review, identifying critical vulnerabilities before deployment, and can undertake lengthy, intricate tasks with remarkable autonomy.
GPT-5-Codex is now live across all existing Codex use cases, including the Codex CLI, IDE extensions, web interface, mobile devices, and GitHub code review. It serves as the default model for cloud-based tasks and code reviews. Developers can also opt to use it for local tasks via the Codex CLI or IDE plugins. Notably, Codex functionalities are integrated into ChatGPT’s Plus, Pro, Business, Edu, and Enterprise subscription tiers.
Within just two and a half hours of its release, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman expressed his excitement, noting that GPT-5-Codex was already accounting for approximately 40% of Codex traffic, a figure he anticipates will become the dominant usage within the day.

“Since the launch of Codex CLI in April and Codex Web in May, Codex has steadily evolved into a more efficient programming assistant,” stated OpenAI. “Two weeks ago, we unified Codex into a single product experience, integrated with ChatGPT accounts. This allows for seamless switching between local environments and cloud tasks without losing context.”
The initial reception has been overwhelmingly positive, with some users hailing it as “the best thing since sliced bread.”
OpenAI has formally incorporated GPT-5-Codex into the GPT-5 System Card as an addendum.

Link: https://openai.com/index/gpt-5-system-card-addendum-gpt-5-codex/
Deep Dive into GPT-5-Codex Capabilities
GPT-5-Codex has been engineered to excel in agentic software engineering within realistic development scenarios.
Its training encompasses sophisticated tasks such as full project construction, feature development, test writing, debugging, large-scale refactoring, and comprehensive code reviews. Compared to the general GPT-5 model, GPT-5-Codex offers enhanced controllability, adheres more precisely to AGENTS.md instructions, and delivers superior code quality. OpenAI commented, “You simply tell it what you want, without needing to write lengthy style guides.”
The model demonstrates superior accuracy over GPT-5 (high) on both the SWE-bench Verified (software engineering) and Code refactoring tasks benchmarks.
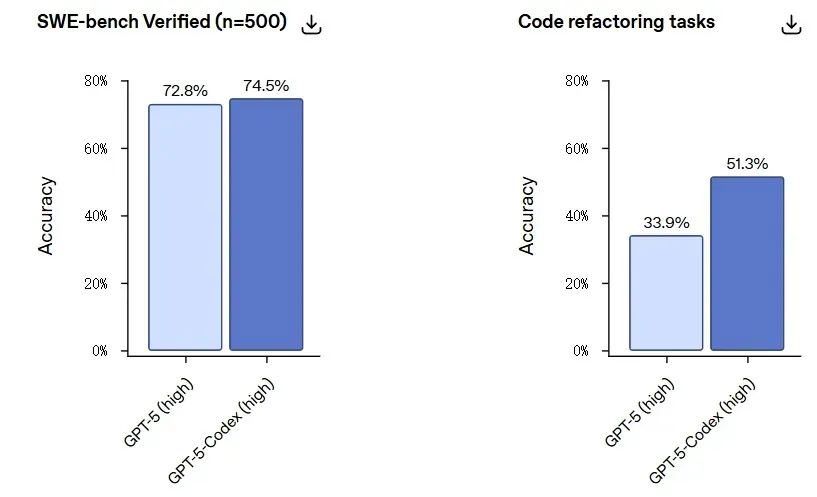
Significantly, OpenAI’s performance on SWE-bench Verified now utilizes all 500 tasks within the dataset, addressing previous criticisms for only using 477 tasks. OpenAI clarified that the prior limitation was due to infrastructure issues that have now been resolved. The Code refactoring tasks benchmark includes refactoring challenges from substantial, mature software libraries across languages like Python, Go, and OCaml. For instance, a pull request for Gitea involved modifying 232 files and 3,541 lines of code to introduce a ctx variable for application logic.
Beyond enhanced performance, GPT-5-Codex dynamically adjusts its processing time based on task complexity. It seamlessly integrates two core capabilities: interactive sessions that collaborate with developers and persistent, autonomous execution for long-running tasks.
For minor requests or conversations, GPT-5-Codex responds with greater speed. Conversely, for intricate tasks like major refactors, it can sustain operations for extended periods. OpenAI reported, “In testing, we observed GPT-5-Codex independently running for over 7 hours, continuously iterating on implementation, fixing tests, and ultimately delivering usable code.”
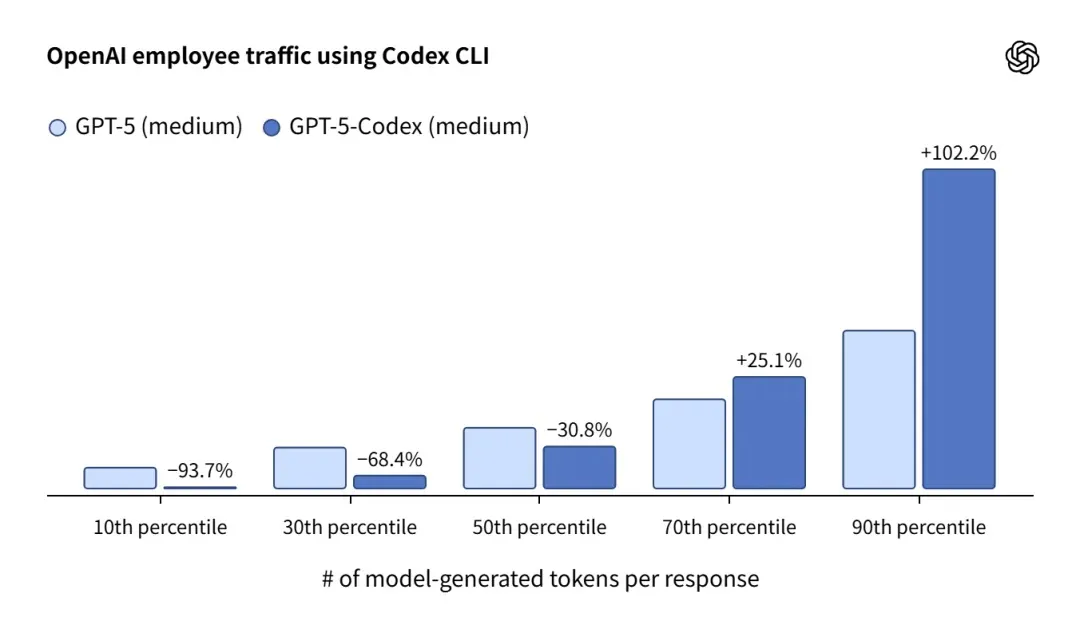
OpenAI shared internal usage data illustrating its efficiency:
- In the bottom 10% of user requests by token consumption (including hidden reasoning and final output), GPT-5-Codex consumed 93.7% fewer tokens than GPT-5.
- In the top 10% of user requests by token consumption, it dedicates more time to in-depth reasoning, editing, testing, and iteration.
GPT-5-Codex has also been specifically trained for code review, proactively identifying critical vulnerabilities. It meticulously analyzes codebases, examines dependencies, and executes code and tests to verify correctness. Evaluations using recent commits from popular open-source projects, validated by experienced engineers, revealed that GPT-5-Codex’s review comments were less prone to errors or irrelevancies, maintaining a focused attention on critical issues.
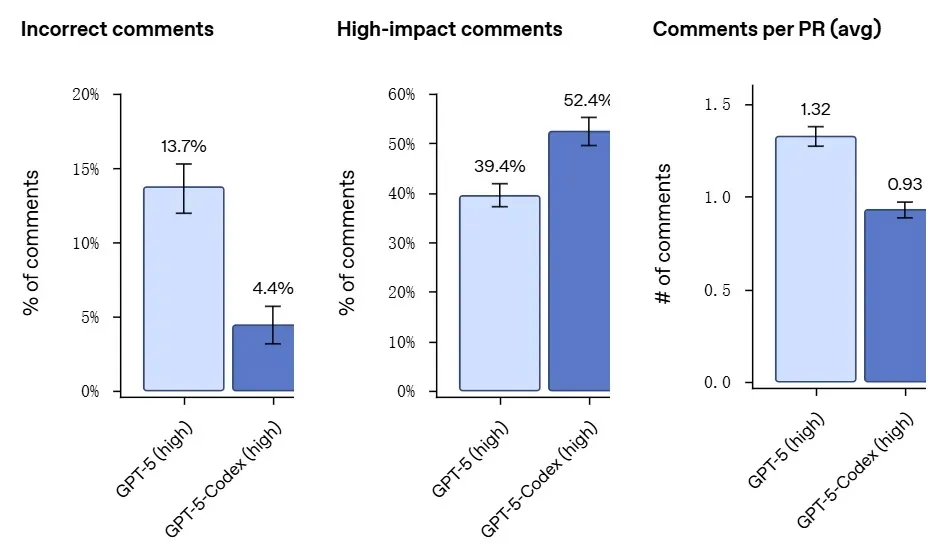
On frontend tasks, GPT-5-Codex exhibits reliable performance, capable of generating aesthetically pleasing desktop applications and significantly improving user experience in preference tests for mobile websites. In cloud environments, it can process uploaded images or screenshots, review its progress, and return screenshots of the results.
While GPT-5-Codex is deeply optimized for Codex CLI, IDE plugins, cloud environments, and GitHub, and supports various tool calls, OpenAI advises, “Unlike the general GPT-5, we recommend using GPT-5-Codex exclusively within Codex or similar scenarios.”
Codex Updates and Enhancements
In addition to the launch of GPT-5-Codex, OpenAI announced several Codex updates, including a redesigned Codex CLI and new Codex IDE plugins.
Codex CLI
The Codex CLI is now open-source. OpenAI has revamped the CLI based on community feedback over recent months to better support “autonomous programming” workflows, making the model a more robust and dependable partner.
Users can now directly include images, such as screenshots, wireframes, and design mockups, within the CLI. This facilitates shared context, clarifies design decisions, and improves the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
For complex tasks, Codex employs a to-do list to track progress and integrates with external systems like web search and MCP, enhancing tool call accuracy.
The terminal interface has also been upgraded for clearer formatting of tool calls and code diffs.
The approval mode has been streamlined into three options:
- Read-only: Requires explicit approval for any modifications.
- Automatic: Grants full workspace permissions but still requires approval for actions outside the workspace.
- Full access: Allows reading any file and executing commands with network access.
The CLI also supports compressed conversation states, simplifying the management of extended sessions.
Codex IDE Plugin
Codex is now directly accessible within IDEs. This plugin supports VS Code, Cursor, and other VS Code derivatives, bringing Codex into the editor for seamless preview of local changes and direct code modifications.
OpenAI highlights several advantages of using Codex within an IDE:
- Shorter prompts, faster results: Codex automatically leverages context, such as open files or selected code, leading to quicker responses.
- Seamless cloud-to-local transitions: Users can create cloud tasks, monitor ongoing work, or review completed tasks directly within the editor.
- Contextual adjustments: Cloud tasks can be opened directly in the IDE for modifications, with Codex preserving the context.
Cloud-Based Codex
Beyond the CLI and IDE plugins, a new GitHub integration brings Codex’s cloud-based intelligence closer to developers’ daily workflows, allowing tasks to be assigned to Codex without leaving the editor or GitHub.
OpenAI has also been enhancing cloud performance behind the scenes:
- Caching containers have reduced task completion times by 90% for new and follow-up tasks.
- Codex automatically detects and executes common initialization scripts to streamline environment setup.
- With network permissions configured, it can execute commands like
pip installduring runtime to install necessary dependencies.
Similar to the CLI and IDE, cloud-based Codex supports image inputs. Developers can upload frontend design specifications or screenshots of UI bugs. Codex will run the generated content within the browser to verify its appearance and attach screenshots to tasks or GitHub PRs.
Code Review Functionality
Codex now includes code review capabilities, designed to identify critical defects. Unlike static analysis tools, Codex performs a comprehensive review by:
- Comparing the pull request’s goals with the actual changes.
- Analyzing the entire codebase and its dependencies.
- Executing code and tests to validate behavior.
This level of scrutiny, typically performed by highly meticulous human engineers, fills a crucial gap, helping teams identify issues earlier, reduce review burdens, and deploy with greater confidence.
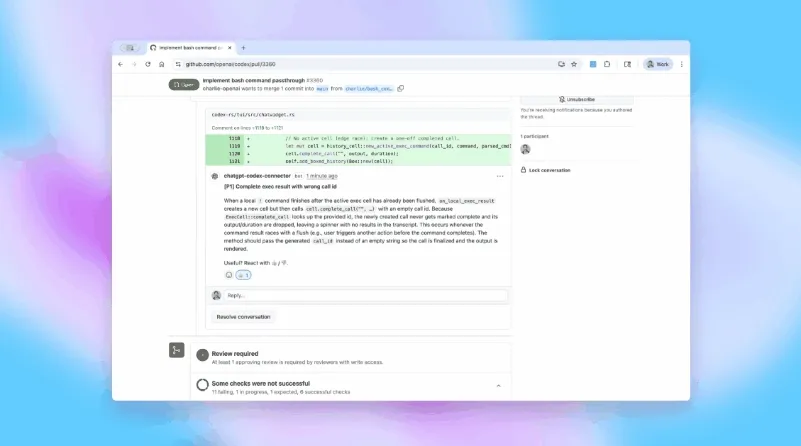
When enabled on GitHub:
- Codex automatically provides analysis when a PR transitions from draft to reviewable status.
- If modifications are suggested, users can directly request their implementation within the same discussion thread.
- Manual review requests can be initiated by typing “@codex review” in the PR, with options for specific requests like “@codex review for security vulnerabilities” or “@codex review for outdated dependencies.”
OpenAI shared, “Internally at OpenAI, Codex has reviewed the vast majority of our PRs, identifying hundreds of issues daily, many of which are caught before human review even begins. This allows teams to move faster while maintaining confidence.”
Ensuring Codex Security
OpenAI has also detailed the security measures implemented during Codex development to protect code and data, along with safeguards against potential misuse.
- Default Sandbox Environment: Both locally and in the cloud, Codex operates in a sandboxed environment by default, with network access disabled. This prevents the execution of harmful operations on user computers and mitigates risks from prompt injection by untrusted sources.
- Permission Mechanisms: Codex requests permission before executing potentially dangerous operations and is trained to run commands to validate its own outputs.
- Configurable Safety Settings: Developers can adjust settings based on their risk tolerance. In the cloud, network access can be restricted to trusted domains. Within the CLI and IDE plugins, developers can decide whether to approve Codex command execution or permit network search and MCP server connections, balancing expanded capabilities with increased risk.
OpenAI advises, “We always recommend developers review Codex’s work before deployment. Codex provides references, terminal logs, and test results for each task to facilitate manual verification.” However, they emphasize that Codex should serve as an additional reviewer, not a complete replacement for human oversight.
Similar to GPT-5, OpenAI classifies tasks in biology and chemistry as “High” capability for GPT-5-Codex and has implemented corresponding safety protocols to minimize potential risks.
Pricing and Availability
Codex is included in ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, Edu, and Enterprise subscriptions.
- Plus, Edu, Business users: Entitled to several intensive coding sessions per week.
- Pro users: Support for a full week’s workload across multiple projects.
- Business plans: Offer the option to purchase additional credits to exceed default limits.
- Enterprise plans: Provide a shared credit pool with pay-as-you-go pricing.
While Codex CLI is not yet accessible via API key, OpenAI has announced that GPT-5-Codex will be available through the API soon.
